3.1. Overview
Presentation
The nextnano.NEGF tool is designed for realistic and accurate quantum simulations of semiconducting devices using the Non-Equilibrium Green Functions (NEGF) formalism. It simulates the electron transport and optical properties of various semiconducting devices consisting of one-dimensional heterostructures such as:
Quantum cascade lasers (QCLs)
Quantum cascade detectors (QCDs)
Resonant tunneling diodes (RTDs)
Quantum-well infrared detectors (QWIPs)
Superlattices (SLs)
Type-II superlattices (T2SL)
Interband cascade lasers (ICLs)
The NEGF formalism is a powerful framework to model quantum transport in the presence of scattering processes. The following scattering mechanisms are included:
Longitudinal optical (LO) phonon scattering
Acoustic phonon scattering
Charged impurity scattering
Interface roughness scattering
Alloy scattering
Electron-electron scattering
An example of application is illustrated below with the calculation of current-voltage characteristics in a QCL.
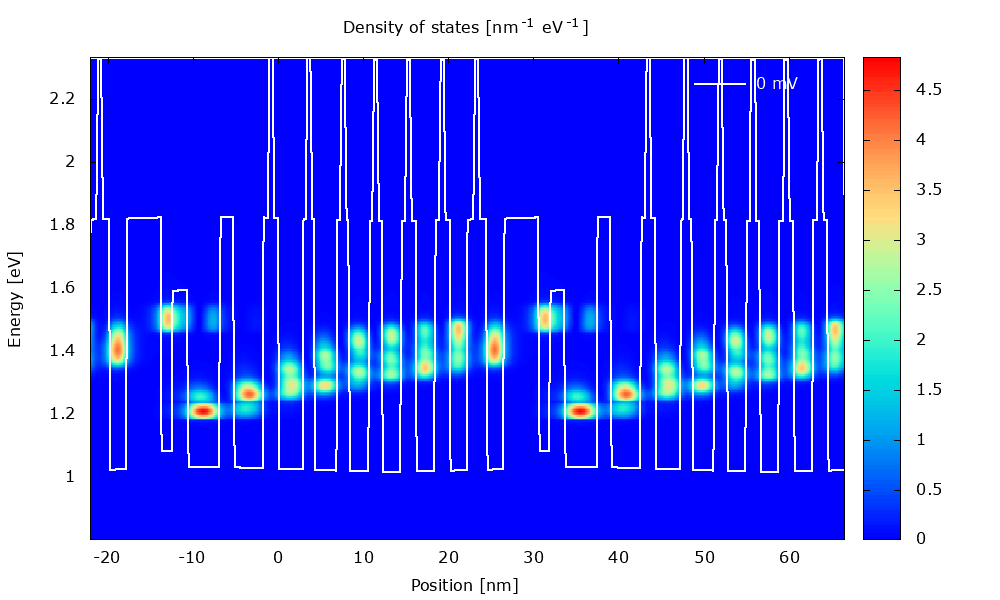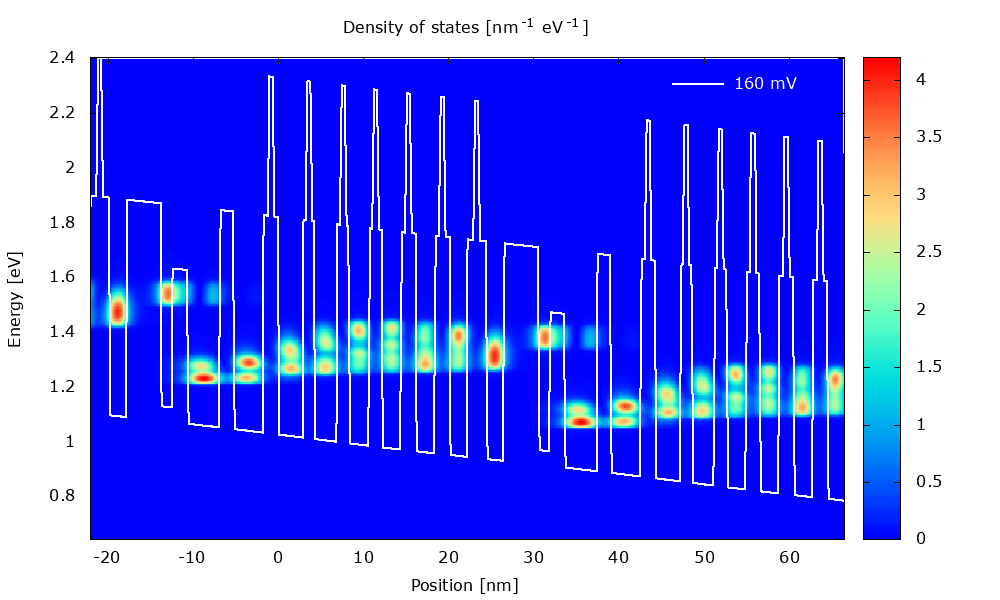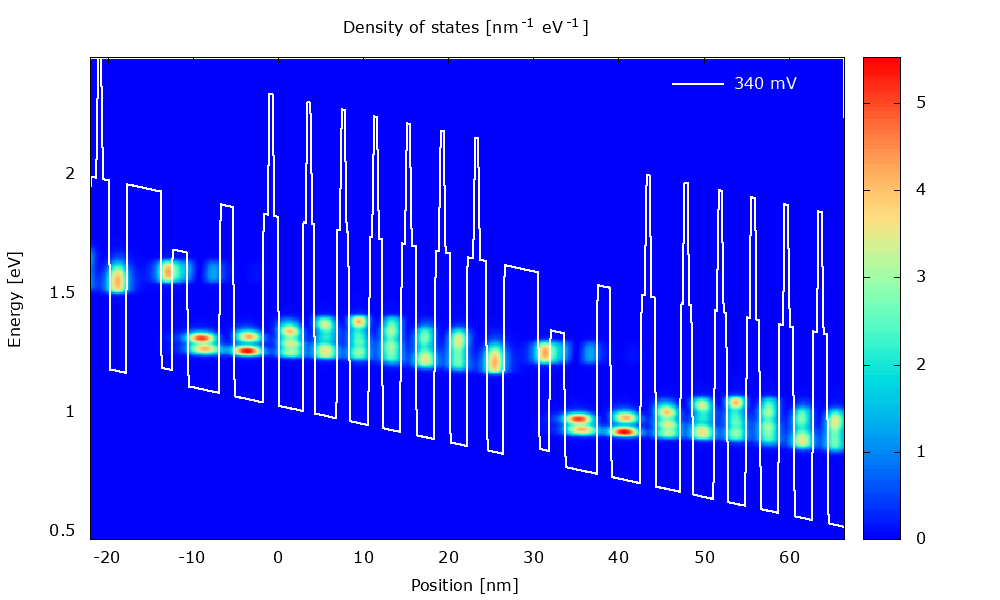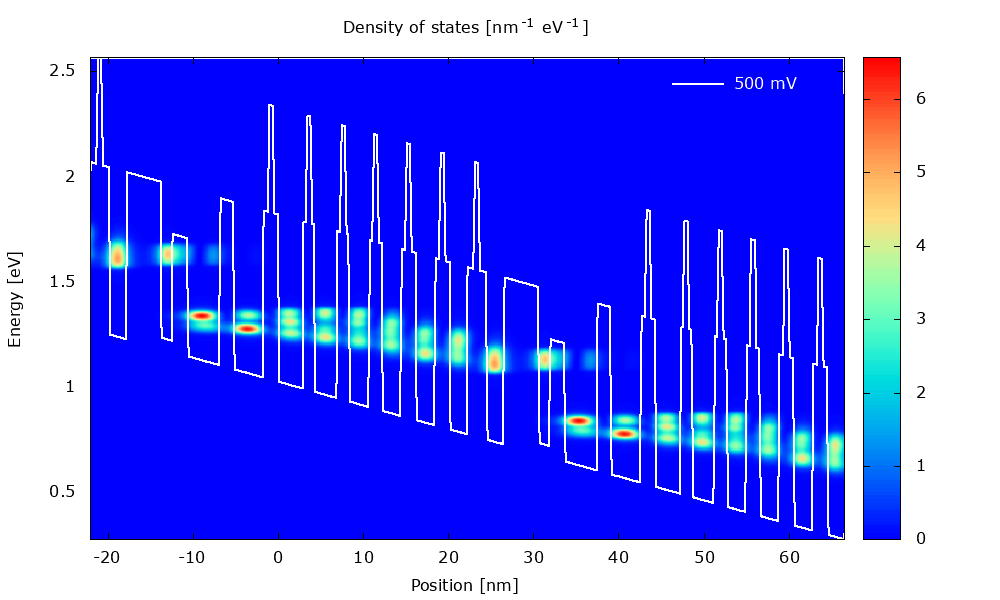
Figure 3.1.1 Local density of states in a QCL structure for varying bias.
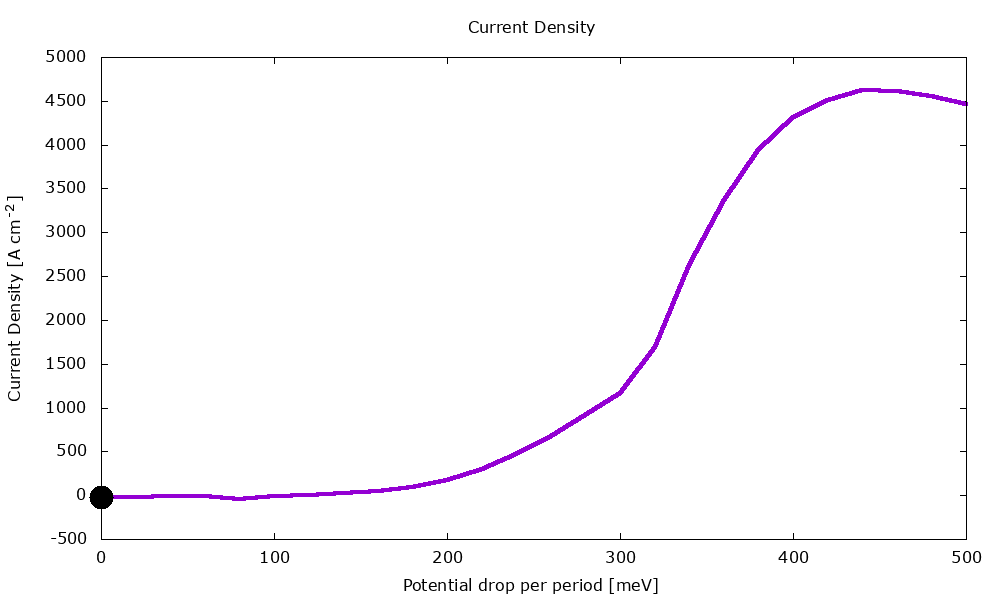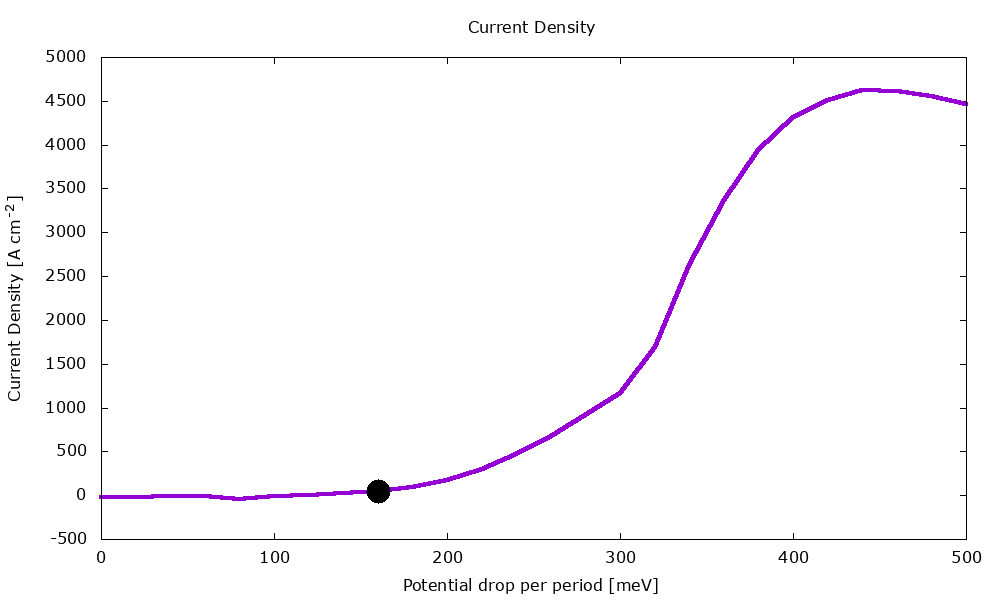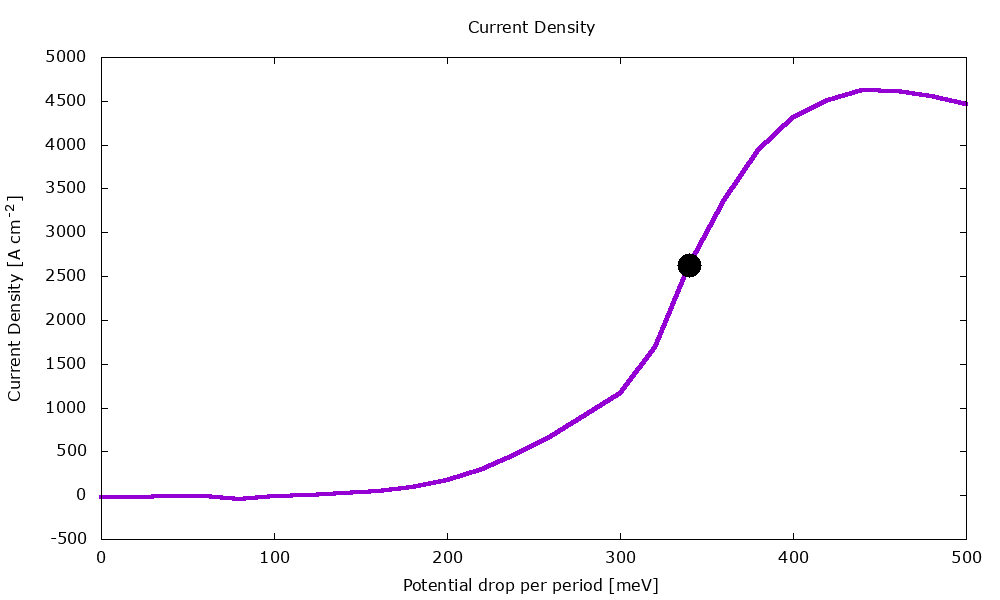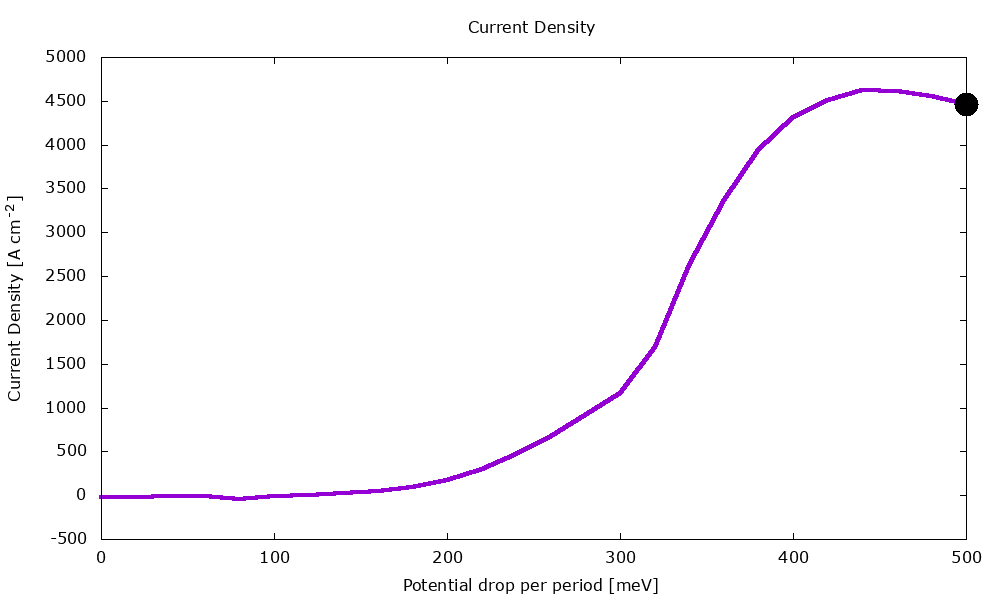
Figure 3.1.2 Current-voltage characteristics of the same QCL structure.
Software Lineup
We offer two versions nextnano.NEGF_classic and nextnano.NEGF. The differences are summarized below:
Version |
nextnano.NEGF_classic |
nextnano.NEGF |
|---|---|---|
Source code language |
C# |
C++ |
Supported operating system |
Windows only |
Windows, Linux* |
Development phase |
Concluded in 2023 |
Since 2022 |
Release notes |
Note
(*) Executables for Red hat Enterprise Linux and macOS will be prepared in the near future.
This documentation describes the new C++ version, which is now the recommended version and includes the latest developed features.
First steps
We recommend downloading bundle packages containing compatible combination of nextnano++, nextnano³, nextnano.NEGF, and nextnanomat. Packages containing only nextnano.NEGF and nextnanomat are also available. The packages are available for Windows and Linux.
We recommend the following steps to kick off:
first get familiar with the nextnanomat user interface using the nextnano++ tool and
then have a look at nextnano.NEGF.
In particular, the Template feature of the nextnanomat user interface is useful. Once you get familiar with the user interface, you are ready to start nextnano.NEGF simulations.
Note
If you have installed nextnano.NEGF separately from nextnanomat, you may need to manually set the path to the nextnano.NEGF.exe executable in
nextnanomat ==> Tools ==> Options ==> Executable ==> nextnano.NEGF executable file for Windows.
Note
On Windows, please make sure to tick the checkbox in Windows File Explorer ==> View ==> File name extensions.
Otherwise, you will only see:
nextnano.NEGF(without file extension.exe) and not
nextnano.NEGF.exe.
Sample input files can be found in the nextnano.NEGF/examples folder. We recommend first running the example Sirtori1994_doubleQW_3bands.negf. It calculates the equilibrium Green’s functions in a double quantum well, and runs within a few seconds. For QCLs, a recommended example to start with is THz_QCL_GaAs_AlGaAs_Fathololoumi_OptExpress2012_10K-FAST.negf. This input file runs fast (typically 5 minutes) and produces a current-voltage characteristics of a THz QCL. More accurate results can be obtained with the corresponding file THz_QCL_GaAs_AlGaAs_Fathololoumi_OptExpress2012-MEDIUM.negf. It takes more time (~2 hours) but produces much more realistic results by including the contribution of high-energy subbands. If the calculation takes much longer, your CPU might not be very fast or you do not have sufficient RAM (see How much memory do I need?).
We hope you enjoy using nextnano.NEGF.
Please let us know if you encounter any difficulty or experience any strange simulation results.
Note
The technical part of the documentation is currently being updated and migrated to here from our old documentation
Last update: 10/12/2024