4.8.4. Ellipsoidal CdSe Quantum Dot
Attention
This tutorial is under construction
- Input files:
QDArtificialAtom_CdSe_3D_spherical_nnp.nnp
QDArtificialAtom_CdSe_3D_ellipsoidal_nnp.nnp
ParabolicQW_GaAs_2D_nnp.nnp
- Scope:
In this tutorial we calculate the eigenenergies of a spherical and ellipsoidal CdSe quantum dot (“artificial atom”). The tutorial is based on [Ferreira2006].
- Output files:
bias00000\Quantum\energy_spectrum_quantum_region_Gamma_00000.dat
bias00000\Quantum\overlap_integrals_quantum_region_Gamma_HH.txt
Energy levels of an “artificial atom” - Spherical CdSe Quantum Dot
Here, we want to calculate the energy levels and the wave functions of a spherical CdSe quantum dot of radius \(r = 5~\mathrm{nm}\) shown in Figure 4.8.4.1.
Figure 4.8.4.1 Spherical quantum dot.
We assume that the barriers at the QD boundaries are infinite. The potential inside the QD is assumed to be 0 eV. We use a grid resolution of 0.5 nm. We solve the single-band Schrödinger equation within the effective-mass approximation. The electron effective mass of CdSe is assumed to be \(m_e = 0.112 m_0\).
A spherically symmetric potential leads to an energy spectrum where some eigenvalues are degenerate. We want to study the “shell structure” (degeneracy scheme) of a CdSe quantum dot of radius 5 nm. Figure 4.8.4.2 shows the calculated energy spectrum for the lowest 20 electron eigenvalues. One can clearly identify the shell structure 1s, 2p, 3d, 2s, 4f and 3p which is similar to the shell structure of the periodic table. This is the reason why quantum dots are often called “artificial atoms”. Note that each eigenstate is two-fold degenerate due to spin. Thus, the s states are two-fold degenerate, the p states are six-fold degenerate, the d states are ten-fold degenerate and the degeneracy of the f states is 14.
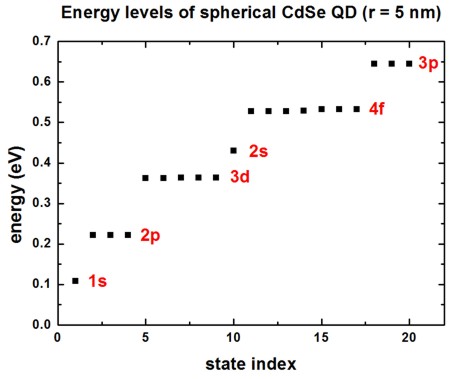
Figure 4.8.4.2 Eigenenergies of the lowest 20 states in the QD.
We have also solved the single-band Schrödinger equation for the holes assuming an isotropic effective mass for simplicity. Obviously, this is a crude approximation. From the electron and hole wave functions, we calculate their spatial overlap matrix elements (overlap integrals). In this simple model, due to symmetry arguments, only the following transitions are allowed: 1s - 1s, 2p - 2p, 3d - 3d, 2s - 2s, 4f - 4f, …
Figure 4.8.4.3 shows the calculated overlap integrals as a function of energy. (Note: The figure has to be updated: Now we output the square of this matrix element.)
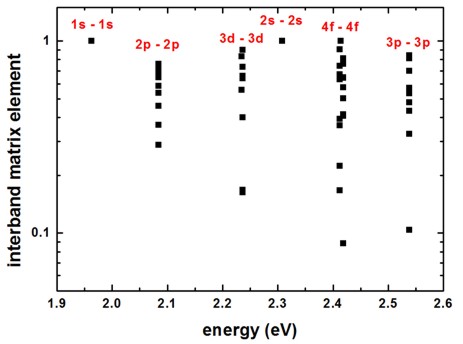
Figure 4.8.4.3 Overlap integrals.
Both figures are in reasonable agreement with Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 (inset) in [Ferreira2006].
Energy levels of an “artificial atom” - Ellipsoidal, cigar-shaped CdSe quantum dot
For an ellipsoidal, cigar-shaped CdSe quantum dot (\(r_x = 5~\mathrm{nm}\), \(r_y = 5~\mathrm{nm}\), \(r_z = 10\mathrm{nm}\)), we calculate the lowest 30 eigenvalues.
Figure 4.8.4.4 Ellipsoidal quantum dot.
The energy spectrum (degeneracy spectrum) looks very different from the spherical QD spectrum (c.f. Figure 4.8.4.5)
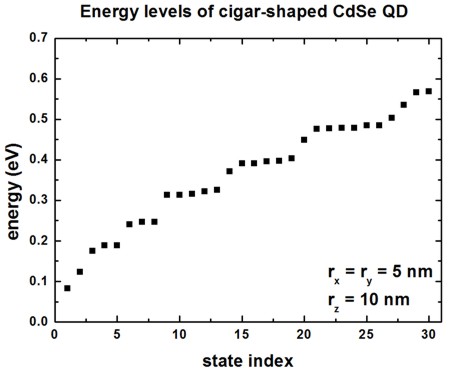
Figure 4.8.4.5 Eigenenergies of the lowest 30 states in the QD.
The overlap integrals are shown in Figure 4.8.4.6 (Note: The figure has to be updated: Now we output the square of this matrix element.)
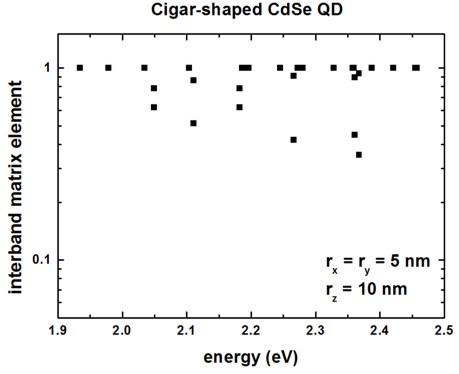
Figure 4.8.4.6 Overlap integrals.
Energy levels of an “artificial atom” - 2D harmonic potential
The following figure shows the energy spectrum of a “two-dimensional disc” which we approximate as a cylindrically symmetric parabolic (harmonic) potential. We solve the 2D Schrödinger equation for this system. The harmonic potential is assumed to be \(\hbar\omega = 3~\mathrm{meV}\). Each shell is thus separated by 3 meV. From the energy spectrum of this two-dimensional shell structure, one can derive “magic numbers”. (They include spin degeneracy.)
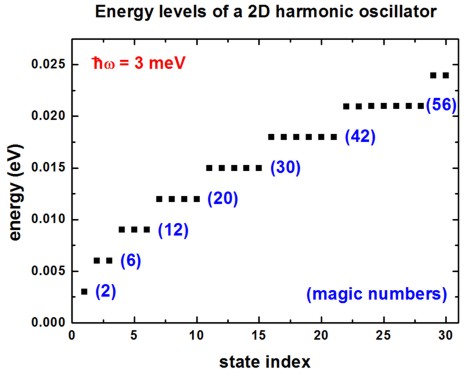
Figure 4.8.4.7 Eigenenergies of the lowest 30 states in a harmonic potential.
This tutorial also exists for nextnano³.
Last update: 2025-10-16